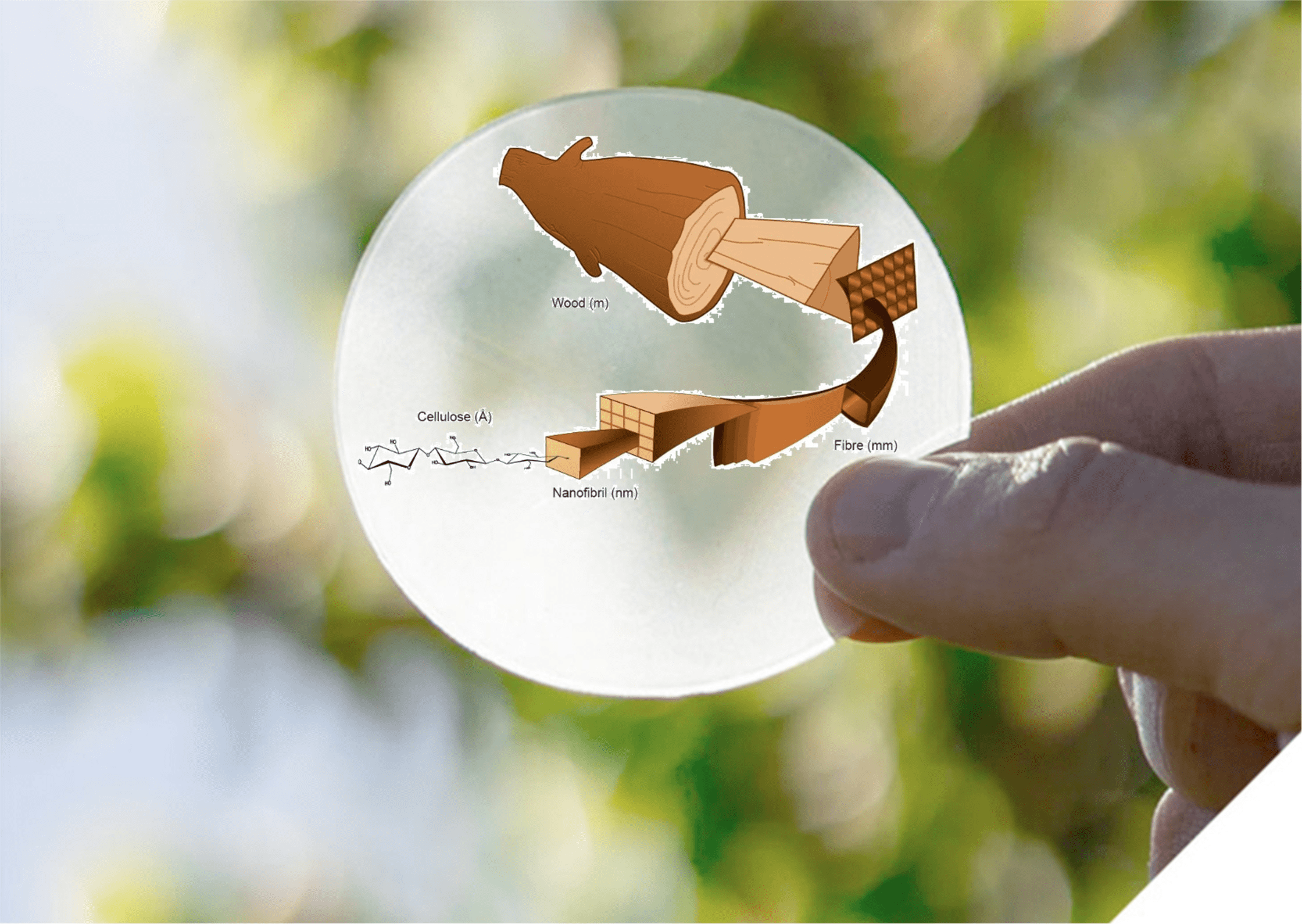
Image source: https://www.cellfion.se/
Trying to study different alternatives regarding one of the most important but conflictive components of RFB, the Ion Exchange Membrane, INO-HUB Energy team contacted Swedish Cellfion company. Cellfion develops nanocellulose derived ion exchange membranes. These membranes could represent a green candidate that could significantly decrease the cost of the whole stack. During the meeting the main requirements for IEM to be implemented in INO-HUB Energy stack were depicted by R&D team.
- Stability: The cellulose-based membrane needs to be stable in the vanadium electrolyte (acid and oxidizing agent).
- Current density: The membrane should operate at high current densities (>200 mA/cm2) showing acceptable energy efficiency (75 %).
- Area Specific Ressitance: The resistance should be around 1 Ohm cm2.
- Crossover: Membrane should exhibit lower or comparable permeabilities values as the current state of the art (Nafion membrane).®
Liam Hardey briefly described their first results and the possibility of sending some samples to INO-HUB Energy facilities to be studied was proposed.
Cellfion membranes present 84% energy efficiency and 99% Coulombic efficiency at 100 mA/cm2 showing the half of capacity decay for VRFB at lab-scale (5 cm2). The main issue could be the water transport observed during this experiment.
So, the preliminary collaboration between both companies was started.
Acknowledgement:
This work was supported by the project: IPCEI_IE_FLOW_BESS_012021